Glucose and Its Properties
Glucose and Its Properties: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Cyclic Structure of Glucose, Open Chain Structure of Glucose, Epimers of Glucose, Pyranose Structure of Glucose, Anomers of Glucose, Chemical Properties of Glucose and, Acetylation of Glucose
Important Questions on Glucose and Its Properties
The products obtained on hydrolysis of sucrose are:
What are the products formed when -glucose is reacted with the following species?
(i)
(ii) Bromine water
Name the reagent and condition required for carrying out of the following reaction
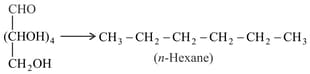
Pentaacetate of D-glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to give oxime.
Explain the reaction of glucose which shows the absence of the free aldehyde group in pentaacetate of D-glucose.
Draw the structure of alpha and beta D-glucose.
Explain the absence of free aldehyde group in the pentaacetate of glucose?
The products and respectively are
The products and respectively are
Which of the following will form the same osazone when treated with excess of phenylhydrazine?
Glucose on treatment with excess of phenyl hydrazine gives
Name of the product formed when glucose reacts with concentrated .
Total number of atoms in ring of pyranose are:
Which of the following is methyl- -glucoside?
(i) 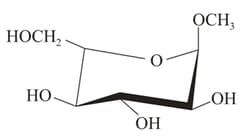
(ii) 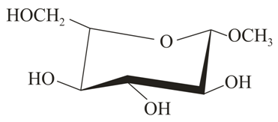
(iii) 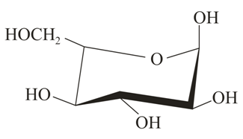
(iv) 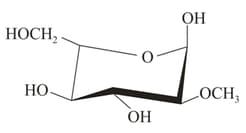
(v) 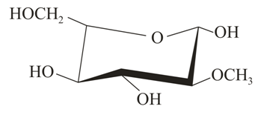
Which of the following statements are correct for glucose:-
How many of the following will produce gluconic acid or it's salt when treated with Glucose
(a) Tollen's reagent
(b)
(c) water
(d)
(e) Fehling's solution
(f) Red
(g) Benedict's solution
(h)
(i)
The _____ form of glucose is optically inactive.
Draw mirror images of glucose and fructose.
